OAuth2 Authentication
Overview
OAuth2 is a protocol that allows you to integrate your application with the Mekari API, which provides more secure authentication and authorization. We provide an authorization code grant type OAuth2 to generate an access token, which can then be used to make requests to the Mekari API. With this grant type, your application will require user authorization because any subsequent API calls made by your application will be on behalf of an existing Mekari User.
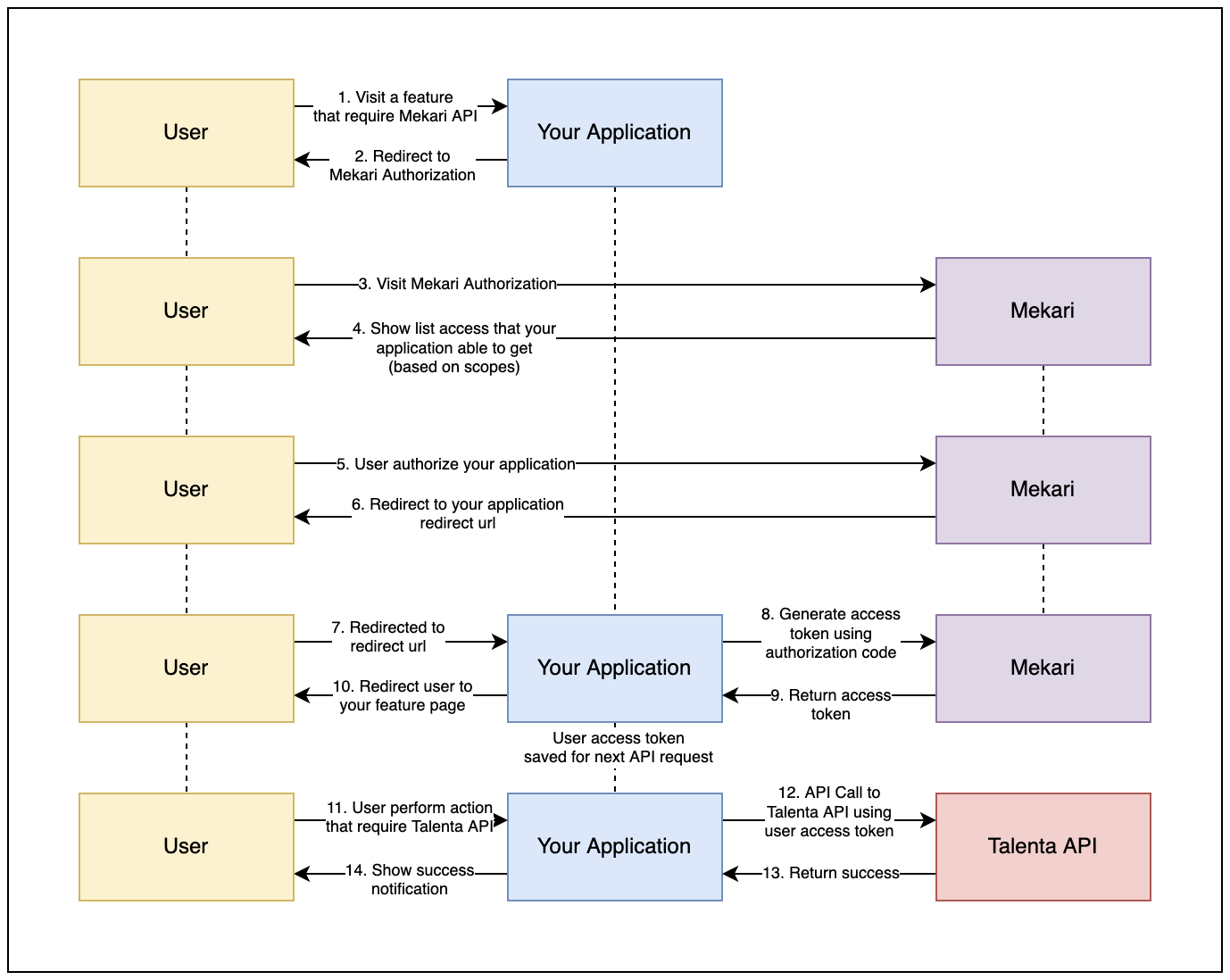
The way it works is that your application must first redirect the user to the Mekari authorization url, from which the user can read all of the permissions that you requested via the scope parameter. If the user decides to authorize your application, the user will be redirected to the url that you specified during application registration as the redirection url. You will then be able to obtain the authorization code, which you can then convert into an access token. Finally, you can use the access token in your application to call the API endpoint.
OAuth2 Credentials
You will need OAuth2 credentials (CLIENT ID and CLIENT SECRET) during the authorization process. We are currently working on a platform that will enable you to generate your own OAuth2 credentials. For the time being, please contact our customer support if you require OAuth2 credentials. We will then assist you in creating new OAuth2 credentials for your application and selecting the appropriate application scopes for the credentials.
API Availability
Not all Mekari product API endpoints can be accessed via OAuth2 authentication. Please visit our Product API section to learn more about the APIs available for OAuth2 authentication.
User Authorization
This is the first step in obtaining the user’s access token for your API call. Your application must redirect the user to the Mekari authorization url using the following parameter:
https://account.mekari.com/auth?client_id={CLIENT_ID}&response_type=code&scope={SCOPES}
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| client_id | The CLIENT_ID of your OAuth2 credential |
| scope | A space-separated list of the scopes that the user must authorize. This also determines which API endpoints can be accessed using the generated access token. |
Once your application request has been approved, the user will be redirected to the application redirect url that you specified during application registration.
Generating Access Token
When the user is redirected to the redirect url, we will add code query parameter to the url that contains an authorization code that can be converted into an access token. If your application redirect url is https://example.com/foo, then the redirection URL will be https://example.com/foo?code=x, where x is the authorization code.
The authorization code can then be used to generate the access token by performing a POST request to https://account.mekari.com/auth/oauth2/token. This is an example of a cURL request:
curl --location --request POST 'https://account.mekari.com/auth/oauth2/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"client_id": "{CLIENT_ID}",
"client_secret": "{CLIENT_SECRET}",
"grant_type": "authorization_code",
"code": "{AUTH_CODE}",
"scope": "{SCOPE}"
}'
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| CLIENT_ID | The CLIENT_ID of your OAuth2 credential |
| CLIENT_SECRET | The CLIENT_SECRET of your OAuth2 credential |
| AUTH_CODE | Authorization code that your application received during authorization process. |
| SCOPE | A space-separated list of the scopes. This value must be same with the one that you set during user authorization process. |
This is an example of a JSON response you will receive after:
{
"access_token": "abc",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "xyz"
}
| key | description |
|---|---|
| access_token | Access token that you can use to make API call. |
| token_type | Type of the token and determining how the token must be used. The value in here will always bearer. |
| expires_in | Time value when the token will be expired in seconds. |
| refresh_token | Token that can be used to generate new access token without performing user authorizaiton. Please see Refresh Token section for more detail. |
The lifetime of an access token is one hour after it is created. When the token expires, you will no longer be able to use it for API requests, and the response will be 401 Unauthorized. If this occurs, you must repeat the user authorization process or use the refresh token to generate a new access token. For more information, please see the Refresh Token section below.
Authorization Header
Once you’ve obtained the access token, you can use it in your application to call the API endpoint. This can be accomplished by using the token on the Authorization header in the following format:
Authorization: Bearer {ACCESS_TOKEN}
ACCESS TOKEN is the token obtained by converting authorization code that has previously been authorized by the user. Following the addition of your access token to the Authorization header, your API request should look like this in cURL format:
curl --request POST 'https://examples.com/foo/bar' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer xxx' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{"hello": "world"}'
Refresh Token
As you may be aware, access tokens have a limited lifetime of one hour and cannot be used again once they have expired. Then your application has two options for getting a new access token: perform new user authorization, which means redirecting the user to the Mekari authorization url again, or use refresh token.
If you use Mekari API in the background and the access token expires, you will be unable to perform a new user authorization process because there is no guarantee the user is on your application. As a result, you may prefer the second option to generate a new access token.
The refresh token has a much longer lifetime than the access token. The refresh token’s lifetime is currently set to 30 days. It means that you can save the refresh token during the user authorization process and use it later to generate a new access token if the old one expires.
To obtain a new access token using a refresh token, make a POST request to https://account.mekari.com/auth/oauth2/token with the refresh token grant type. This is an example of a cURL request:
curl --location --request POST 'https://account.mekari.com/auth/oauth2/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"client_id": "{CLIENT_ID}",
"client_secret": "{CLIENT_SECRET}",
"grant_type": "refresh_token",
"refresh_token": "{REFRESH_TOKEN}",
"scope": "{SCOPE}"
}'
| parameter | description |
|---|---|
| CLIENT_ID | The CLIENT_ID of your OAuth2 credential |
| CLIENT_SECRET | The CLIENT_SECRET of your OAuth2 credential |
| REFRESH_TOKEN | Refresh token that you get from previous access token generation request. |
| SCOPE | A space-separated list of the scopes. This value must be same with the one that you set during user authorization process. |
This is an example of a JSON response you will receive after:
{
"access_token": "abc",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 3600,
"refresh_token": "xyz"
}
As you can see, requesting a new access token with a previous refresh token results in a new refresh token that can be used to obtain the next access token if your current access token expires. The refresh token itself can only be used once, which means that once you’ve successfully used it to generate a new token, you won’t be able to use it again in the future.